The format and the style of the objectives differs from one another based on the requirements. However, there is a baseline that should be followed while drafting objectives. The first thing that needs to be done before writing objectives is that you need to clearly analyze all your options and then give it a shape. At times; people think that objectives are same as resumes, but they are nothing like it.
Objectives are useful for each industry and business that is interested in improving their current projects and operations to reach the desired results. Project outcomes should be a direct result of the project objectives your organization sets. Writing effective project objectives helps your business to operate more efficiently and maintain a high level of organization.
In this article, we discuss what project objectives are, what you should and should not include in your objectives and how to write your own with examples.
Table of Contents
What are project objectives?
Project objectives are objectives made in an organization to assist with the successful completion of a project to achieve specific project management goals within a set timeframe. The project objectives should be in alignment with the overall industry objectives and assist with solving issues in a company’s problem statement.
Project objectives also provide your team with communication that will assist them with executing projects in a way that demonstrates quality work and pleases the stakeholders of your company.
How to write project objectives
When you write your project objectives, there are a few steps you can take to make the process more efficient and provide you with clear and concise objectives.
- Identify which systemic behaviors or conditions need to be changed.
- Define what success means for your project.
- Describe the focus group.
- Include the location and time period.
- Narrow down your objectives.
1. Identify which systemic behaviors or conditions need to be changed
There may be challenges with the system or team member behaviors that prevent a project objective from being as efficient as possible. Assess former projects and identify the behaviors or conditions that can be changed to streamline the next project.
Identifying these issues helps you to prioritize the project objectives you should begin writing first. It provides you with a foundation to build objectives that are SMART or specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time-bound. This will lead you to create the right objectives that assist with success.
2. Define what success means for your project
You must define the reason why you are creating your project objective and then define what it would mean to successfully complete the project objective. This helps you to determine how long the objective takes to complete for the given project, what you are interested in achieving and how you and your team can go about resolving any challenges that may arise concerning the objective.
The best way to define what success means to your overall project is to write down the possible outcomes and challenges by doing a SWOT analysis. The SWOT analysis helps you measure a project’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
3. Describe the focus
Describing the focus means providing detailed information about the focus of your objective. This doesn’t necessarily mean a group of people, but rather any part of the business that affects your project or projects. Your focus may be leads, websites, systems, customer surveys, turnover, sales, profitability, etc.
For example, if your company wants to become more sustainable by reducing the amount of plastic waste, then you can say that your focus is sustainability. Research and describe your company’s current sustainability to gain a better understanding of how a project objective can help your team to achieve the desired results.
The focus is likely different for each objective and you should describe details about the focus and then you can see if your focus is a realistic priority that is in line with organizational objectives and goals.
For example, if your company wants you to focus on profitability but you choose to set an objective to reduce plastic waste and increase sustainability to become a more eco-friendly company. It may potentially increase manufacturing costs and reduces profitability for your company and therefore you may want to rethink that specific project objective.
4. Include the location and time period
This step means identifying when and where the objective should be completed. Objectives may include many different departments and require a vast amount of teamwork to complete successfully. This means that the objectives must be organized and specific, which includes adding the location and time period. The location means including where you would like this objective to take place such as in the district, region, nation or at a specific branch. The time period suggests the date when an objective should be completed such as the third quarter, annually, etc.
5. Narrow down your objectives
There may be a decent amount of information you must consider before writing your objective. However, it is important to narrow your objectives and make them as brief as possible while including all the necessary information that will assist your team with the successful completion of the objectives. The best way to do this is to write them down a couple of different ways before you settle on the final objective.
How to Write Objectives in a Research Proposal
Method 1: Brainstorming Your Objectives
- State your main research question to guide your ideas. If you’re writing a research proposal, then you’ve probably developed a research question. To figure out your objectives, state that question clearly and concisely. Analyze that question and consider the steps you’d have to take to answer it.[1]
- For example, your research question might be “What is the effect of prolonged TV-watching on children?” You can then use that question to build your study around.
- Narrow down your research topic if it’s too broad. A broad research topic makes breaking the objectives down much more difficult. A research question like “How can we save the environment?” is a huge question. Something like “What safety measures would prevent ocean pollution?” is more specific and attainable.[2]
- Describe the ultimate goal of your study. Consider what you want your research project to achieve. This is similar to your research question but should state the intended results more definitively. For example, if you were measuring the effects of prolonged TV-watching on children, you could say “This study will tell parents and healthcare providers how much TV time is safe for children under age 5.” Deciding on your intended results helps develop your objectives.
- Remember that in most cases, you shouldn’t state that your study will prove or disprove something exactly since you haven’t done the work yet. Don’t say “This study proves that honey is not an effective treatment for acne.” Instead, make it something like “This study will demonstrate whether or not honey is an effective treatment for acne. ”Break that goal down into sub-categories to develop your objectives. In most cases, your ultimate goal will be large enough to break down into smaller steps. These steps from the foundations of your list of objectives. Look at your research question and stated goal and think about what steps you’d take to answer them.[4]
- If your research question was “What is the effect of prolonged TV-watching on children?” then there are a few categories you could look at. Objectives wrapped up within that question might be: 1) the incidence of eyestrain among children who watch a lot of TV, 2) their muscular development, 3) their level of socialization with other children. Design your objectives around answering these questions.
- Limit your objectives to 3 to 5 at most. Trying to achieve too many objectives makes your project unwieldy, and you could get overwhelmed. Keep your objective list limited to 3 to 5 specific aims. That way, your project is substantial enough to answer important questions, but not so large that you can’t complete it.
- You could always state in your research proposal that you plan to design future experiments or studies to answer additional questions. Most experiments leave unanswered questions and subsequent studies try to tackle them.
- Divide your objectives into 1 general and 3-4 specific ones. In many research proposals, the proper format is a general or long-term objective followed by a few specific ones. The general objective is essentially what you hope to achieve with the project. The specific objectives are the building blocks of that general goal. Divide the two categories for a well-focused and planned research project.
- A general objective might be “Establish the effect of diet on mental health.” Some specific goals in that project could be 1) Determine if processed foods make depression worse, 2) Identify foods that improve mood, 3) Measure if portion sizes have an impact on mood.
- Not all research proposals want you to divide between general and specific goals. Remember to follow the instructions for the proposal you’re writing.
- Assess each objective using the SMART acronym. This acronym stands for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, and Time-bound. It’s a common tool for all kinds of goal-setting and is a great guide for assessing your research objectives. Run all of your objectives through this test to see how strong they are. Eliminate or revise weak objectives.
- The best goals align with each letter in the SMART acronym. The weaker ones are missing some letters. For example, you might come up with a topic that’s specific, measurable, and time-bound, but not realistic or attainable. This is a weak objective because you probably can’t achieve it.
- Think about the resources at your disposal. Some objectives might be doable with the right equipment, but if you don’t have that equipment, then you can’t achieve that goal. For example, you might want to map DNA structures, but you can’t view DNA without an electron microscope.
- Ask the same question for your entire project. Is it attainable overall? You don’t want to try to achieve too much and overwhelm yourself.
- The specific words in this acronym sometimes change, but the sentiment is the same. Your objectives should overall be clear and specific, measurable, feasible, and limited by time.
Method 2: Using the Right Language
- Start each objective with an action verb. Objectives are about action, so use verbs when you list them. Think of strong action verbs to start each objective with. This makes your proposal look actionable and dynamic.
- Verbs like use, understand, or study is vague and weak. Instead, choose words like calculate, compare, and assess.
- Your objective list might read like this: 1) Compare the muscle development of children who play video games to children who don’t, 2) Assess whether or not video games cause eyestrain, 3) Determine if videogames inhibit a child’s socialization skills.
- Some proposals use the infinitive form of verbs, like “to measure” or “to determine.” This is also fine but refer to the proposal instructions to see if this is correct.
- State each objective clearly and concisely. Your objective should be 1 sentence at most. Use clear, simple, and actionable language so your readers can follow and understand your goals.
- You can further explain your objectives further in the research proposal. No need to elaborate a lot when you’re just listing them.
- If you’re having trouble shortening an objective to 1 sentence, then you probably need to split it into 2 objectives. It might also be too complicated for this project.
- Use specific language so readers know what your goals are. Objectives don’t need to be packed with specific data, but they should have enough detail that readers know exactly what you’re studying. Be as clear as you can so readers don’t have any uncertainties about what you’re working on.
- For example, “Determine if sunlight is harmful” is too vague. Instead, state the objective as “Determine if prolonged sun exposure increases subjects’ risk of skin cancer.”
- It’s helpful to let someone else read your proposal and see if they understand the objectives. If they’re confused, then you need to be more specific.
- State your objectives as outcomes rather than a process. This is a small change, but it makes your proposal look more confident and actionable. Try to describe the objectives as definitive answers rather than questions. Confident language like this makes your proposal stronger.
- For example, don’t say “Measure the effect of radiation on living tissue.” Instead, say “Determine what level of radiation is dangerous to living tissue.”
- Remember, don’t state the objectives as you’ve already done the experiments. They’re still not answered.Advertisement
Method 3: Writing the Objectives
- Insert your objectives after your introduction and problem statement. In a normal research proposal format, you’ll start with an introduction and statement of your problem or question. This lays out the structure and direction of the project. After these parts, then list your objectives. Each of these sections should have a clear section headings, so start the objectives section with “Objectives” in large, bold text.
- This is a common format for research proposals, but not universal. Always follow the format that the instructions provided.
- Depending on how long your introduction has to be, you might also list the objectives there. This depends on whether or not you have room.
- Note the objectives in the proposal abstract if you have one. Some research proposals have an abstract in the beginning. This is essentially a detailed summary of the proposal. If you’re instructed to include an abstract, then briefly note the objectives in it. This way, readers can tell the direction of the project right from the start.
- At the very least, the abstract should list the general objective. This tells the readers what your study is working towards.
- Introduce the section with your general objective first. Start off the objectives section with a few sentences about the project and its ultimate goal. In this introduction, state the general objective clearly, which is what you want the project to achieve. Introduce your objectives section with this general objective before getting more specific.
- In some research projects, the general objective is called a long-term goal instead. Adjust your language to the proposal requirements.
- Some proposals directions may just want the specific objectives rather than a division between the general and specific ones. Don’t divide them if the instructions tell you not to.
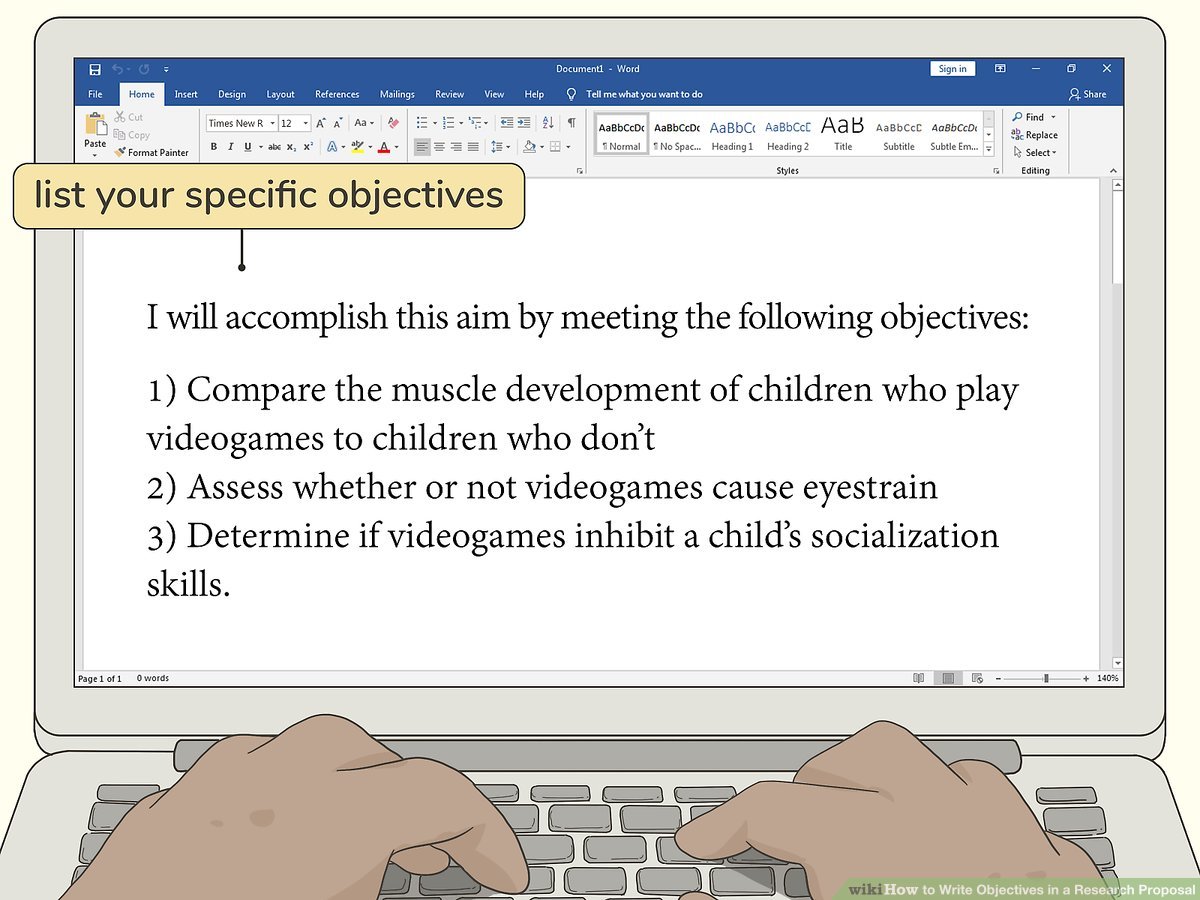
- List your specific objectives next. If you’ve already decided on your objectives, then this part is easy. Start a numbered list after your introduction and give each objective its own number. Remember that each objective should be 1 sentence max and start with action verbs. Keep the language clear and concise so readers can tell exactly what your goals are.
- Your introduction may be as follows:
“My long-term objective with this project is determining whether or not prolonged video-game playing is harmful to children under 5. I will accomplish this aim by meeting the following objectives:
1) Compare the muscle development of children who play videogames to children who don’t
2) Assess whether or not videogames cause eyestrain
3) Determine if videogames inhibit a child’s socialization skills” - The specific objectives are usually listed as a bullet or numbered points. However, follow the instructions given.
- Your introduction may be as follows:
Conclusion
Objectives are your goals or major aims about what you want to achieve. Because of having so many objectives, it is important that you list all of them but do not put too much time and consideration into each item on the list. Well-organized and specific objectives will lay the foundation for a thriving business.