How to Write Interval Notation – Have you ever found yourself studying for a mathematics, music, or science test and forget how to write interval notation? I know the feeling, it’s hard to retain all of the interval notation formulas in one sitting. That’s why I made this article where I provide examples of interval notation symbols, and even interval notation solver so that you have the tools to complete the assignment with ease. I hope you enjoyed this post!
We use interval notation to represent subsets of real numbers. Suppose that a and b are real numbers such that a < b.
Then, the open interval (a,b) represents the set of all real numbers between a and b, except a and b.
- { x / a < x < b} is the set-builder notation.
- a < x < b is the inequality description.
- (a, b) is the interval notation.
The closed interval [a,b] represents the set of all real numbers between a and b, including a and b.
- { x / a ≤ x ≤ b} is the set-builder notation.
- a ≤ x ≤ b is the inequality description.
- [a, b] is the interval notation.
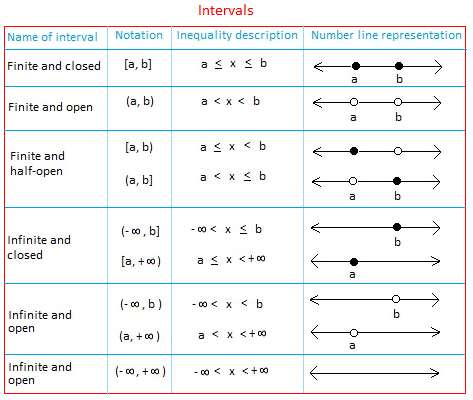
The table below lists nine types of intervals used to describe subsets of real numbers. Notice the number line representation of each interval.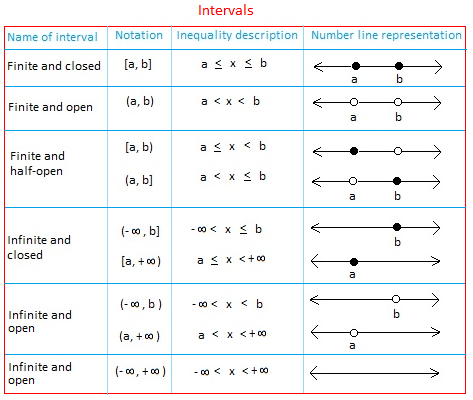 35Save
35Save
Basically, an interval is a set containing all numbers between two given numbers or endpoints. The set may have one, both, or neither of the two given numbers.
An interval is open if the interval does not contain its endpoints.
The symbols ( or ) are used to indicate that an endpoint is not included in the interval.
An interval is closed if the interval contains its endpoints.
The symbols [ or ] are used to indicate that an endpoint is included in the interval.
Sometimes, the interval may contain only one of its endpoints. In this case, the interval is half-open. The interval [2, 8) is half-open. It contains 2 and all numbers between 2 and 8. Notice that 8 is not included since the interval is open at 8.Notice the symbol ∞ which mean infinity.
-∞ means minus infinity and +∞ means positive infinity.
Both -∞ and +∞ are used to show that an interval is unbounded or extends indefinitely to the left or to the right respectively.
Why do we need intervals? They can be used to describe the domains of functions, bounds for estimates, and the solution sets of equations and inequalities.
The length of an interval with endpoints a and b with a < b is b – a.
Table of Contents
Converting an inequality to interval notation
Express each inequality in interval notation.
Examples
Inequality Interval notation
-6 ≤ x < 1 [-6, 1)
x > 20 (20, ∞)
x ≥ -1 or x < -4 (-∞, -4) U [-1,∞)
What do you Mean by Interval Notation?
Interval notation is a method to represent any subset of the real number line. We use different symbols based on the type of interval to write its notation. For example, the set of numbers x satisfying 1 ≤ x ≤ 6 is an interval that contains 1, 6, and all numbers between 1 and 6.
What is Interval Notation on a Graph?
When we represent the solution set of an interval on a number line, that is a graph for the interval notation.
How to Graph Interval Notation using Number Line?
We can graph the interval notation for a given set of numbers based on the type of number and specific symbols for the brackets used to enclose the set for the given particular type.
What is the ∪ Symbol for Interval Notation?
The union “∪” symbol is used to denote the union of two or more intervals in any Interval notation. Interval notation is defined as the method used to represent any subset of the real number line.
What are the Types of Intervals?
There are different types of intervals that can be represented by following a different set of rules for interval notation. These types of interval notation can be given as,
- Open Interval
- Closed Interval
- Half-Open Interval
How to Convert Inequality to Interval Notation?
We can convert inequality to interval notation using the below-given steps,
- Firstly, we need to graph the solution set of the interval on a number line.
- Then write the numbers in the interval notation with a smaller number appearing first on the number line on the left.
- Use the symbol “-∞” for the unbounded set on left and if it is unbounded on right, use the symbol “∞”.
How do you Exclude Numbers in Interval Notation?
We use the round brackets to exclude numbers in interval notation. These numbers are generally the endpoints of the given set. To exclude a set of numbers in between, we can use two different sets and club them together using the union symbol ‘∪’.
Conclusion
What is interval notation? Interval notation, also known as the number line, is a system of representing real numbers with points on a line. It commonly appears in set theory where the set of real numbers forms an uncountable set (that is, too large to count), which makes it challenging to write using standard notation.