How to Solve Unemployment – Unemployment is a global issue which happens in developed, underdeveloped and developing countries. The major evidence is that even the developed countries are battling with unemployment issues.
A survey has suggested that in 2013 December, about 6.7% of Americans were unemployed.
The international labor organization has mentioned the statistics of both employed and unemployed in 2012 which states that about 6% of the world population are unemployed and youths are the ones who are unemployed i.e youth unemployment.
The government and individuals should take proper remedy steps to solve the unemployment problem and develop the nation’s economy through employment.

Table of Contents
What is Unemployment?
Unemployment can be defined as when an individual is hunting for employment and does not find a job, then unemployment arises.
Unemployment is one of the major crises that happens around. The term unemployment measures the economy’s health.
The unemployment rate is usually used for measuring unemployment. It is usually the unemployed individuals divided by a number of labor force people.
The reports as per the international labor organization said that about 200 million globally or about 6% of the complete workforce was unemployed in 2012.
In that manner let’s glimpse through a few aspects of unemployment and the various aspects related to it.
Unemployment Statistics:
The unemployment rate reached a post during World War II to a high of 9.7% in 1982. The data regarding unemployment and earnings was captured by the Department of Labor’s Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
There were other reports too which mentioned the unemployment rate of 9.6% in the year 1983 which was due to an economic recession. This was after the great depression of 1983. It was in 1989 that the unemployment rate dropped to 5% but started enhancing again. This led to 6.8% in 1991 and to 7.5% in 1992.
Once there was an enhancement in an economy, the unemployment rate fell to 6.9% in 1993. The good news was that the unemployment rate fell to about 4.5% in 1998 and to 4% in 2000 which was considered as the lowest in three decades.
It was in 2001 that recession crept in and unemployment rates rose again and then the terrorist attack on September 11, 2001, in the United States was also a reason of unemployment. By 2003 June, about 9.4 million was unemployed where the unemployment rate was elevated to 6%. There was again a decline in the unemployment rate from 2003 to 2007.
The fluctuation started again and there was a rise in the year 2007 and the unemployment rate was 4.9% in 2008 January. People without a job and looking for work are counted as unemployed. It does not include people who have lost their jobs and not looking for it.
Types of Unemployment:
With the many causes of unemployment, the prime causes of unemployment are listed below. People fall under one of these categories as a reason for unemployment. Some of the types of unemployment are as follows:
1. Structural unemployment:
At times when there is a mismatch of skills in the work industry this unemployment occurs. Some of them are partitioned as mentioned below.
- Geographical immobility:Geographical immobility type of unemployment happens due to the difficulty the individual faces in shifting to other regions for a job. For example, jobs may be available in California but it might be tough to get accommodated or find appropriate schooling for children.
- Occupational immobility:Occupational immobility kind of unemployment occurs when a candidate is unable to learn new skills which need to be applied in the new industry along with a change in technology. A simple example can be that a farmer unable to work in high technological industries.
- Technological change:There are many industries which possess the labor-saving technology and have led to falling in labor. This has been the main reason for unemployment after the technology has advanced.
- Structural change in economy:The structural change that happens in a nation is another reason for this unemployment. For example, the weakening of coal mines because of the absence of competitiveness has made a number of coal mine workers unemployed. These people cannot find jobs in any new industries which includes computers and technology.
2. Frictional unemployment:
This type of frictional unemployment prevails in many countries. This type of unemployment is the period which is taken by the individuals while they change their job. Examples are graduates who try to find another job. It surely takes time in order to find another job.
3. Real wage or classical unemployment:
This type of unemployment takes place when the wages in the competitive job market moves above equilibrium.
For example, when the supply of labor is higher than the demanded labor, this type of unemployment takes place. Times when trade unions and labor organizations bargain for higher wages are when this type of unemployment occurs. This leads to a decline in demand for labor.
4. Voluntary unemployment:
Voluntary kind of unemployment is one where people try to be unemployed than being employed. A simple example can be that if individuals are able to get a good benefit, then they prefer to stay back with the benefit rather than being employed.
Frictional unemployment also falls under this category where individuals tend to choose a job until they wanted an appropriate one.
5. Cyclical unemployment or Demand deficient:
The demand deficient or cyclical unemployment takes place when the economy falls below its full capacity. A simple example can be the aggregate demand which falls below at times of recession which leads to weakening in negative economic growth and output.
When there is a drop in the output then the employment of workers will also be less which leads to the development of fewer goods.
There are many firms which move out of the business and result in redundancies in large-scale. There are more workers being laid off during recessions which lead to unemployment.
6. Seasonal unemployment:
This is one category of unemployment which takes place due to seasonal change in the job nature. Few industries that are affected by seasonal unemployment are catering industries, fruit picking, tourism, and hospitality.
7. Youth unemployment:
Youth unemployment is another major concern that is happening. 73 million people are globally neither unemployed nor undertaking education.
Youth unemployment is three times ahead of the elders. In the US, the youth unemployment rate is about 5.7% and about 17% of the nation’s youth are jobless.
8. Casual Unemployment:
Casual employment is the type of employment that comes in, for employees who work on a day to day basis or on short term contracts. When the contract is completed, the employee will get unemployed and that type is known as casual unemployment.
This type of unemployment would not stand for long, as the workers get another contract work or the earlier work gets extended. Most of the places where casual employment exists for people are dockyards, market places, film industry (junior artists), etc.
Here the work of the workers gets completed or lasts for just a few hours or day long and then they get back to the same unemployment position. This process goes on until they find a permanent job. It is very difficult to provide a definite solution to such casual unemployment issue.
9. Chronic Unemployment:
This type of unemployment is mainly seen in undeveloped countries. When a country is suffering long term of unemployment on a whole, then it is known as chronic unemployment. Some of the main reasons of chronic unemployment are,
- Weak economic condition
- Lack of developed resources
- High population growth
- Primitive state of technology
- Low capital formation, etc.
Effects of Unemployment:
Unemployment effects in nations lead to a number of hassles, in that manner let’s glimpse through a few effects of unemployment.
1. Few tax revenues:
Due to unemployment, there are fewer people who work and earn money and hence only less income tax would be collected. There would be less tax revenue collected by the government and would have a large impact on government finances.
2. High supply-side cost:
Due to unemployment, there would be a number of people who do not work. The government needs to teach the employees with skills that are required for the present industry conditions.
So it is the duty of the government to spend by training skills so that they match with the latest industry. This is a drain on the government’s economy due to unemployment.
3. Enhanced welfare cost:
During the unemployment period, few people would work but almost all people would claim for benefits.
Due to this, the government money is drained again. Government finance is used for providing benefits for people.
4. Lower wages:
At times of unemployment, there is an increased supply of labor for employment in firms. In this scenario, there is a decline in wages as there is a number of people ready to work for lower wages.
By this way, the industries have a positive effect and their variable cost would decline.
5. Surplus labor:
Due to the impact of unemployment, there are a number of candidates ready to work and hence, the industries have enhanced choice for employment. They choose skilled labors with more experience.
6. Enhanced demand for inferior goods:
Few goods in an economy are purchased more at times of lower-income for individuals and these are mentioned as inferior goods.
During the unemployment period, people switch over to purchase more of inferior goods due to low income. Inferior goods owner would have a higher profit and sales revenue.
7. Goods and services on less demand:
Unemployment makes individuals avoid buying goods and services as they possess a very low income. In such scenarios, there is lower sales revenue that leads to a decline in profits.
8. Elevated training cost:
Though there are many firms that benefit themselves from low wage cost as a result of unemployment, they also need to spend and train employees as they have been out of work for a long period.
Training employees are accomplished with the firm’s resources and time hence, there is an increase in the employee’s cost.
9. Lower living standards:
Private savings and benefits are the only sources which people rely on at times of unemployment. They do not spend much and buy only fewer goods for their living and hence, they are pushed to a lower standard of living.
10. Loss of depression and confidence:
Unemployment is a period where people are pushed to depression and loss of confidence. It also affects one’s mental and physical health. Almost all people who are unemployed are lead to stress-related depression and also ill most of the time.
11. Loss of skills:
Skills and capability to work are lost by individuals during the unemployment period. The prolonged period a person is unemployed, the more the industries have to train them in order to make them work.
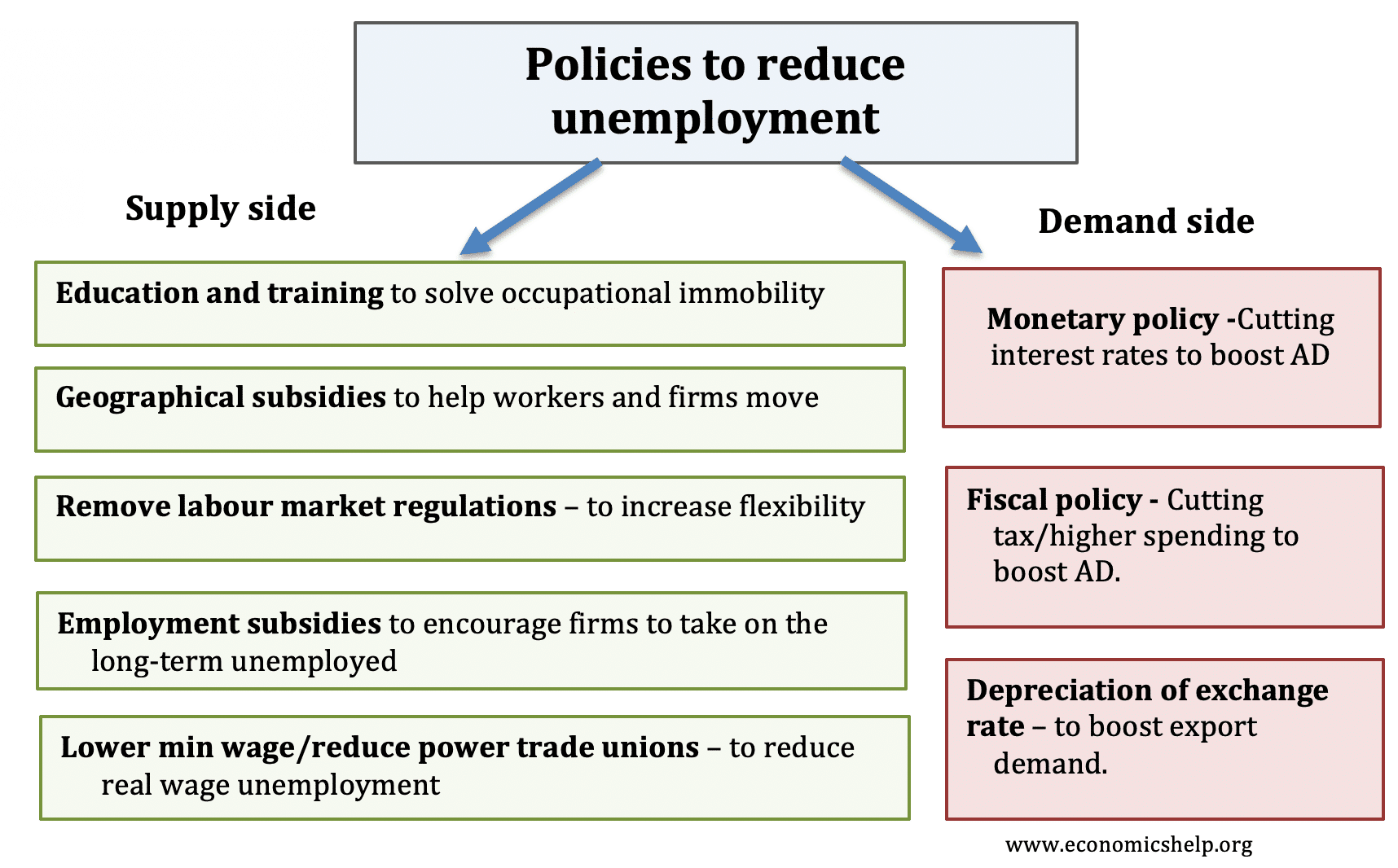
How to Solve Unemployment
The solution for unemployment is, of course, to create new jobs. The number of jobs that need to be created depends on the unemployment rate and the number of people entering the labor force in search of work. When unemployment creeps above 6% to 7% and stays there, it means the economy can’t create enough new jobs. That’s when the government steps in.1
For historical data on U.S. unemployment trends, the Bureau of Labor Statistics publishes the unemployment rate by year.2 It reports the annual percentage of the unemployed in the labor force, as far back as 1949. It also indicates the success or failure of the fiscal and monetary policies through the years, since they affect the rate of unemployment.
Monetary Policy
The first solution is expansionary monetary policy from the Federal Reserve. It’s powerful, quick, and effective. Lower interest rates make it easier for families to borrow what they need. That includes expensive items like cars, homes, and consumer electronics. It stimulates enough demand to put the economy back on track. Low-interest rates also allow businesses to borrow for less. That gives them the financial capital to hire enough workers to meet rising demand.3
Fiscal Policy
If the recession is really severe, then monetary policy might not be enough on its own. That’s when fiscal policy is needed. The government can either cut taxes or increase spending to stimulate the economy. An expansionary fiscal policy is slower than monetary policy to get started. It takes time for Congress and the president to agree on the next steps. But it can be more effective once executed. It also provides much-needed confidence that the government will turn things around. Confidence is crucial for convincing people to spend now for a better future.4https://b04494971456c11d93222862e262936e.safeframe.googlesyndication.com/safeframe/1-0-38/html/container.html
Cutting taxes works like lowering interest rates. Both give businesses and consumers more money to spend. That increases demand. It gives businesses more cash to invest and hire more workers. https://b04494971456c11d93222862e262936e.safeframe.googlesyndication.com/safeframe/1-0-38/html/container.html
Government spending can also take the form of jobs programs. The government can hire employees directly. It also contracts with companies to build things and provide services.5 It provides consumers with the cash they need to buy more products.6
The Most Cost-Effective Solution
Dollar for dollar, what’s the best investment that creates the most jobs? A University of Massachusetts Amherst study found that building mass transit is the most cost-effective solution. One billion dollars spent on public transportation creates 19,795 construction jobs.7
Unemployment benefits can provide growth as well. According to Wayne Vroman, an economist and senior fellow at the Urban Institute for the Department of Labor, unemployment insurance led to the creation of 1.6 million jobs on average each quarter from 2008 to 2010.8 The unemployed are most likely to spend every dime they get. They buy basics like groceries, clothing, and housing. As a result, every dollar spent on unemployment benefits stimulates $1.64 in Gross Domestic Product.9
How can $1 create $1.64? It does it through the ripple effect. For example, a dollar spent at the grocery store pays for the food. It also helps pay the clerk’s salary, the truckers who haul the food, and even the farmers who grow it. The clerks, truckers, and farmers then buy groceries. This ripple effect keeps demand strong, creating added benefits. Stores keep their employees to supply the goods and services the unemployed need. Without these benefits, demand would drop. Then retailers would need to lay off their workers, increasing unemployment rates. https://b04494971456c11d93222862e262936e.safeframe.googlesyndication.com/safeframe/1-0-38/html/container.htmlhttps://b04494971456c11d93222862e262936e.safeframe.googlesyndication.com/safeframe/1-0-38/html/container.html
Unemployment benefits work fast. The government writes a check that goes directly into the economy. Public works projects take longer to get implemented. The plans must be updated, workers hired, and supplies delivered.
Funding education is also an effective unemployment solution. One billion dollars spent hiring teachers adds $1.3 billion to the economy. Better-educated people can get higher-paying jobs. They can buy more things with the higher wages they earn. Each $1 billion spent can create 17,687 jobs. That’s much better than defense spending. It only creates 8,555 jobs for the same investment. Defense is more capital-intensive. Modern defense relies more on drones, F-35s, and aircraft carriers than soldiers.7
The most popular fiscal stimulus is across-the-board income tax cuts. That’s not the most cost-effective, according to the UMass/Amherst study. One billion dollars in cuts creates 10,779 jobs. Workers only spend half the money, which in this case is only $505 million.
As a result, reductions in the tax rate are not the most effective way to help job growth. Most people don’t realize they are getting a break until tax time. The tax cut means they pay less in taxes, but they still have to pay. Psychologically, they are less likely to spend anything extra. It just doesn’t feel like a bonus. As a result, people are more liable to save anything they get or use it to pay down other debts.1011
A more effective tax cut is in businesses’ payroll taxes. The best place to give business tax relief is with small businesses. From 2000 to 2018, they produced 65% of all net new jobs created.12
Fiscal Policy Risks
The downside of fiscal policy is that it could add to the budget deficit. That creates more government debt. As debt approaches 100% of the economy’s total output, it slows economic growth. Investors could lose the desire for that government’s debt. This makes interest rates rise, increasing the cost of borrowing.13
Advocates of supply-side economics say that, over time, tax cuts boost the economy enough to replace any lost tax revenue. But according to the Laffer Curve, that’s only true if taxes are over a certain threshold to start with.14
The Bottom Line
The government uses two policies to tackle unemployment: monetary and fiscal.4
Expansionary monetary policy increases the money supply and:
- Has more immediate effects.
- Stimulates demand, production; and ultimately, employment.
- Is managed by the Federal Reserve or a central bank.3
Expansionary fiscal policies include government spending and tax cuts. These:
- Take more time to have an impact.
- Have a greater impact on consumerism, so they are more effective as economic stimuli.
- Unfortunately, they increase government debt and add to the budget deficit.
The most cost-effective solutions are fiscal. Building mass transit, granting unemployment benefits, funding the educational sector, and payroll tax cuts allow consumers to gain more income which they spend to spur demand.
Conclusion
The growth of population should be checked in order to solve unemployment, problem. Family planning programme should be implemented widely and effectively.