Python comes with a variety of built-in data structures, capable of storing different types of data. A Python dictionary is one such data structure that can store data in the form of key-value pairs. The values in a Python dictionary can be accessed using the keys. In this article, we will be discussing the Python dictionary in detail.
Table of Contents
Creating a Dictionary
In Python, a Dictionary can be created by placing a sequence of elements within curly {} braces, separated by ‘comma’. Dictionary holds pairs of values, one being the Key and the other corresponding pair element being its Key:value. Values in a dictionary can be of any data type and can be duplicated, whereas keys can’t be repeated and must be immutable.
Note – Dictionary keys are case sensitive, the same name but different cases of Key will be treated distinctly.
Python3
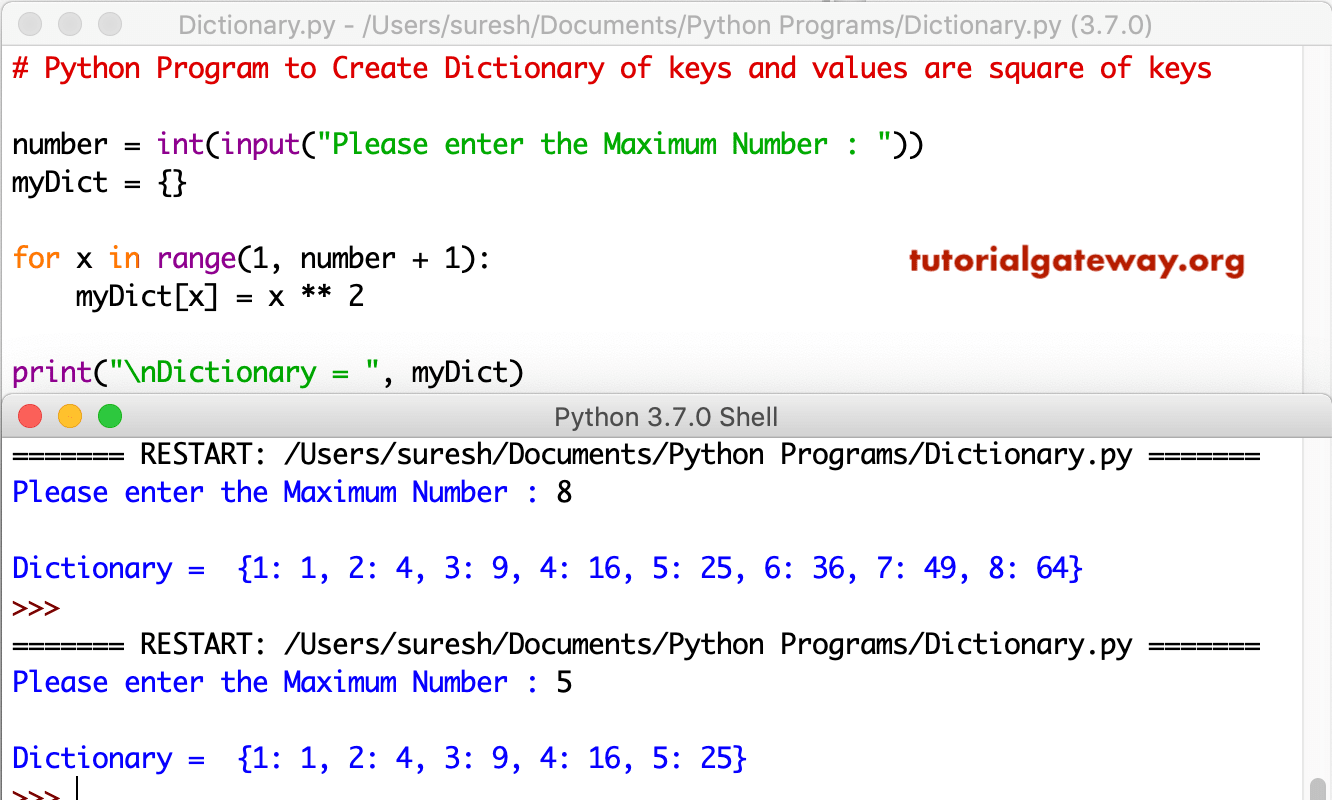
# Creating a Dictionary# with Integer KeysDict = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}print("\nDictionary with the use of Integer Keys: ")print(Dict) # Creating a Dictionary# with Mixed keysDict = {'Name': 'Geeks', 1: [1, 2, 3, 4]}print("\nDictionary with the use of Mixed Keys: ")print(Dict) |
Output:
Dictionary with the use of Integer Keys:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Dictionary with the use of Mixed Keys:
{1: [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Name': 'Geeks'}
Dictionary can also be created by the built-in function dict(). An empty dictionary can be created by just placing to curly braces{}.
Python3
# Creating an empty DictionaryDict = {}print("Empty Dictionary: ")print(Dict) # Creating a Dictionary# with dict() methodDict = dict({1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3:'Geeks'})print("\nDictionary with the use of dict(): ")print(Dict) # Creating a Dictionary# with each item as a PairDict = dict([(1, 'Geeks'), (2, 'For')])print("\nDictionary with each item as a pair: ")print(Dict) |
Output:
Empty Dictionary:
{}
Dictionary with the use of dict():
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Dictionary with each item as a pair:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For'}
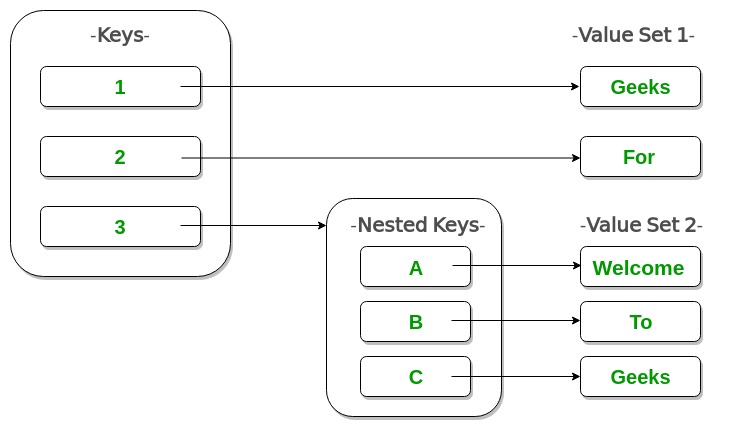
Nested Dictionary:
Python3
# Creating a Nested Dictionary# as shown in the below imageDict = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3:{'A' : 'Welcome', 'B' : 'To', 'C' : 'Geeks'}} print(Dict) |
Output:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: {'A': 'Welcome', 'B': 'To', 'C': 'Geeks'}}
Adding elements to a Dictionary
In Python Dictionary, the Addition of elements can be done in multiple ways. One value at a time can be added to a Dictionary by defining value along with the key e.g. Dict[Key] = ‘Value’. Updating an existing value in a Dictionary can be done by using the built-in update() method. Nested key values can also be added to an existing Dictionary.
Note- While adding a value, if the key-value already exists, the value gets updated otherwise a new Key with the value is added to the Dictionary.
Python3
# Creating an empty DictionaryDict = {}print("Empty Dictionary: ")print(Dict) # Adding elements one at a timeDict[0] = 'Geeks'Dict[2] = 'For'Dict[3] = 1print("\nDictionary after adding 3 elements: ")print(Dict) # Adding set of values# to a single KeyDict['Value_set'] = 2, 3, 4print("\nDictionary after adding 3 elements: ")print(Dict) # Updating existing Key's ValueDict[2] = 'Welcome'print("\nUpdated key value: ")print(Dict) # Adding Nested Key value to DictionaryDict[5] = {'Nested' :{'1' : 'Life', '2' : 'Geeks'}}print("\nAdding a Nested Key: ")print(Dict) |
Output:
Empty Dictionary:
{}
Dictionary after adding 3 elements:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 1}
Dictionary after adding 3 elements:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4)}
Updated key value:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'Welcome', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4)}
Adding a Nested Key:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'Welcome', 3: 1, 5: {'Nested': {'1': 'Life', '2': 'Geeks'}}, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4)}
Accessing elements from a Dictionary
In order to access the items of a dictionary refer to its key name. Key can be used inside square brackets.
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate # accessing a element from a Dictionary # Creating a DictionaryDict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'} # accessing a element using keyprint("Accessing a element using key:")print(Dict['name']) # accessing a element using keyprint("Accessing a element using key:")print(Dict[1]) |
Output:
Accessing a element using key: For Accessing a element using key: Geeks
There is also a method called get() that will also help in accessing the element from a dictionary.
Python3
# Creating a DictionaryDict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'} # accessing a element using get()# methodprint("Accessing a element using get:")print(Dict.get(3)) |
Output:
Accessing a element using get: Geeks
Accessing an element of a nested dictionary
In order to access the value of any key in the nested dictionary, use indexing [] syntax.
Python3
# Creating a DictionaryDict = {'Dict1': {1: 'Geeks'}, 'Dict2': {'Name': 'For'}} # Accessing element using keyprint(Dict['Dict1'])print(Dict['Dict1'][1])print(Dict['Dict2']['Name']) |
Output:
{1: 'Geeks'}
Geeks
For
Removing Elements from Dictionary
Using del keyword
In Python Dictionary, deletion of keys can be done by using the del keyword. Using the del keyword, specific values from a dictionary as well as the whole dictionary can be deleted. Items in a Nested dictionary can also be deleted by using the del keyword and providing a specific nested key and particular key to be deleted from that nested Dictionary.
Note: The del Dict will delete the entire dictionary and hence printing it after deletion will raise an Error.
Python3
# Initial DictionaryDict = { 5 : 'Welcome', 6 : 'To', 7 : 'Geeks', 'A' : {1 : 'Geeks', 2 : 'For', 3 : 'Geeks'}, 'B' : {1 : 'Geeks', 2 : 'Life'}}print("Initial Dictionary: ")print(Dict) # Deleting a Key valuedel Dict[6]print("\nDeleting a specific key: ")print(Dict) # Deleting a Key from# Nested Dictionarydel Dict['A'][2]print("\nDeleting a key from Nested Dictionary: ")print(Dict) |
Output:
Initial Dictionary:
{'A': {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}, 'B': {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'Life'}, 5: 'Welcome', 6: 'To', 7: 'Geeks'}
Deleting a specific key:
{'A': {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}, 'B': {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'Life'}, 5: 'Welcome', 7: 'Geeks'}
Deleting a key from Nested Dictionary:
{'A': {1: 'Geeks', 3: 'Geeks'}, 'B': {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'Life'}, 5: 'Welcome', 7: 'Geeks'}
Using pop() method
Pop() method is used to return and delete the value of the key specified.
Python3
# Creating a DictionaryDict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'} # Deleting a key# using pop() methodpop_ele = Dict.pop(1)print('\nDictionary after deletion: ' + str(Dict))print('Value associated to poped key is: ' + str(pop_ele)) |
Output:
Dictionary after deletion: {3: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For'}
Value associated to poped key is: Geeks
Using popitem() method
The popitem() returns and removes an arbitrary element (key, value) pair from the dictionary.
Python3
# Creating DictionaryDict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'} # Deleting an arbitrary key# using popitem() functionpop_ele = Dict.popitem()print("\nDictionary after deletion: " + str(Dict))print("The arbitrary pair returned is: " + str(pop_ele)) |
Output:
Dictionary after deletion: {3: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For'}
The arbitrary pair returned is: (1, 'Geeks')
Using clear() method
All the items from a dictionary can be deleted at once by using clear() method.
Python3
# Creating a DictionaryDict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'} # Deleting entire DictionaryDict.clear()print("\nDeleting Entire Dictionary: ")print(Dict) |
Output:
Deleting Entire Dictionary:
{}
Dictionary Methods
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| copy() | They copy() method returns a shallow copy of the dictionary. |
| clear() | The clear() method removes all items from the dictionary. |
| pop() | Removes and returns an element from a dictionary having the given key. |
| popitem() | Removes the arbitrary key-value pair from the dictionary and returns it as tuple. |
| get() | It is a conventional method to access a value for a key. |
| dictionary_name.values() | returns a list of all the values available in a given dictionary. |
| str() | Produces a printable string representation of a dictionary. |
| update() | Adds dictionary dict2’s key-values pairs to dict |
| setdefault() | Set dict[key]=default if key is not already in dict |
| keys() | Returns list of dictionary dict’s keys |
| items() | Returns a list of dict’s (key, value) tuple pairs |
| has_key() | Returns true if key in dictionary dict, false otherwise |
| fromkeys() | Create a new dictionary with keys from seq and values set to value. |
| type() | Returns the type of the passed variable. |
| cmp() | Compares elements of both dict. |
Conclusion
Dictionary in Python is an unordered collection of data values, used to store data values like a map, which, unlike other Data Types that hold only a single value as an element, Dictionary holds key:value pair. Key-value is provided in the dictionary to make it more optimized.